Your website could sport a very professional design but unless that site is not ranking well in search engines, it may be tough for new and potential customers to discover your business on the Internet.
Therefore, when planning to create an online presence for your brick and mortar business, it is extremely important that your site layout and content is optimized for search engines.
If you are wondering why the title says “Google friendly” where there are exist so many other search engines on the Internet (including popular ones like Yahoo!, Ask and MSN), that’s because Google has the reach like no other.
Most website owners would agree that Google alone drives 90-95% of traffic to their websites.
There are basically two ways to drive visitors from Google to your website – one, you buy ads that show up on Google results pages for certain keywords (using AdWord) or two, work hard to get good rankings in search results (organic traffic). While the former method costs money, organic traffic is free but requires effort and understanding of how search engines work.
We’ll focus on techniques and guidelines that will help improve the rank of our web pages in organic search results. And though we mention only Google, the techniques do apply to all other search engines as well. Let’s get started:
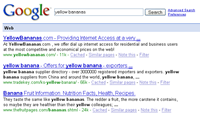
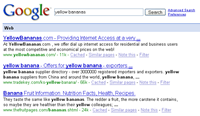
Always write clean and descriptive titles – When people scan (nobody reads word by word) the different results on a search page, that first thing that will catch their attention is the title of your web page. Similarly, if X is looking for “yellow bananas” on Google, web pages that contain this term in the title are likely to rank higher. A good title could look something like “Yellow Bananas | Green Grocery Store”
Construct keyword rich URLs – Like Titles, search engines always favor web pages that contain relevant keywords in the URLs of the web page. Continuing with our previous “yellow bananas” example, a URL like abc.com/products/fresh-yellow-bananas.htm or abc.cm/products/yellow-bananas.htm will always perform better than something like abc.com/products?id=232 or abc.com/products/232.html
Use Meta Tags – Meta tags (keywords & descriptions) were important in the good old AltaVista days but not anymore since they were so easy to abuse and search engines devised better algorithms to rank web pages. However, good descriptions in Meta tags can really help bring search traffic because they appear as short snippets in search pages beneath your page title. If a meta tag is missing, Google could display some other text page from the web page that may not always be very relevant.
Win Incoming Links – Other than quality content and a good site structure, incoming links from other websites are also essential for your site to rank high in search engines. And the best way to get those links is to write content that’s informative and adds value. For instance, not many people may know but bananas can be used to remove scratches from old CD and DVD disks. Such tips can easily go viral in the web community and may win you lot of incoming links.
Google Sitemaps – You can also consider creating a sitemap of your website and submit that to Google Webmaster Central – the advantage here is that Google will be able to discover and index some web pages on your site that exist but enjoy no link love and hence search bots cannot discover them during regular crawling.
Text, Text, Text – Web page elements like Flash animations, images and videos clips could make your site look very attractive but the problem is that all search engines can only read text. If you avoid using text, search engines will never know the actual context of web pages and that will affect your rankings.
Underground SEO practices – Do not participate in link exchange programs and never buy links with the purpose of inflating your PageRank. Also, avoid stuffing irrelevant keywords in your web pages as all these “SEO tricks” may lead to penalties or even a site being removed entirely from the Google index.
Duplicate Content – Always make sure that all pages on your website have unique content. When you serve two or more pages with similar content to search engines, they will have trouble deciding which page should rank higher than the other and it could therefore dilute your search rankings.
[via labnol.org]